What is Static seal?
Static seal
A static seal is usually a seal between two stationary faces. So-called static seal refers to a seal that is in a stationary state during bearing operation without relative motion. A seal that does not move relative to each other between seal couplers is referred to as a static seal. A seal that does not have a relative movement between the two coupling members of the static sealing portion is referred to as a static seal.
Introduction to static sealing
Static seal
Static seal vocabulary Interpretation Static seals usually refer to the seal between two stationary faces.
Static seal static seal type
Static seals mainly include three types: pad seal, sealant seal and direct contact seal. According to the working pressure, the static seal can be divided into a medium-low pressure static seal and a high-pressure static seal. Medium and low pressure static seals are commonly used for gaskets with a wide softer width, while high pressure static seals use metal gaskets with a narrower material contact width. [1]
Static sealing static sealing material
Static sealing gasket material
Non-metallic materials: such as paper, hemp, cowhide, asbestos products, plastics, rubber, etc. Paper, hemp, cowhide and the like, with pores, easy to penetrate, must be immersed in oil, wax or other anti-penetration materials. Typical valves are rarely used. Asbestos products, asbestos tape, rope, board and asbestos rubber sheet. Among them, the asbestos rubber sheet has a compact structure, good pressure resistance and good temperature resistance, and is widely used in the valve itself and the flange connection of the valve and the pipe. Plastic products have good corrosion resistance and are commonly used. The varieties are polyethylene, polypropylene, soft polyvinyl chloride, polytetrafluoroethylene, nylon 66, nylon 1010 and the like. Rubber products, soft texture, all kinds of rubber have certain acid, alkali, oil and sea water resistance. The varieties include natural rubber, styrene butadiene rubber, nitrile rubber, neoprene rubber, butyl rubber, urethane rubber, and fluoro rubber. [1]
Static sealing metal materials Generally speaking, metal materials have high strength and high temperature resistance. But lead is not like this, only taking its resistance to dilute sulfuric acid. Commonly used varieties are brass, copper, aluminum, low carbon steel, stainless steel, monel, silver, nickel and so on. [1]
Static sealing polymer sealing material
The sealant is a sealing material that is applied between the two joint faces to block the leak gap. The sealant is a polymer sealing material. Sealant is generally divided into two types: liquid sealant and anaerobic glue. The sealant has good sealing performance, good temperature resistance, pressure resistance, dense medium resistance, etc. It is easy to use, and is often used for sealing between static joint surfaces of electromechanical products and sealing of complicated joint surfaces. . [1]
The performance of the sealing material requires that the sealing material meet the sealing function requirements. Sealing materials are required to have different applicability due to the different media being sealed and the different working conditions of the equipment. The requirements for the sealing material are: 1 the material has good compactness and is not easy to leak the medium; 2 has suitable mechanical strength and hardness; 3 has good compressibility and resilience, and has small permanent deformation; 4 does not soften or decompose under high temperature, and is low temperature No hardening, no brittle cracking; 5 good corrosion resistance, long-term work in acid, alkali, oil and other media, its volume-hardness change is small, and does not adhere to the metal surface; 6 friction coefficient is small, wear resistance Good; 7 has a softness with the sealing surface; 8 good aging resistance, durable. [1]
Static seals seals between stationary parts in industrial applications machines (or equipment). A common form is to place a gasket between the flanges. This seal is called a flange gasket type forced seal (Figure 1). Tighten the bolts to compress the gaskets to block the leaking gap for sealing purposes. The material and form of the gasket are selected according to the operating temperature of the equipment, the pressure and the corrosiveness of the medium. For example, rubber gaskets can be used for normal temperature, medium and low pressure equipment, PTFE gaskets can be used for equipment working at low temperature or corrosive working medium, asbestos rubber gaskets can be used for higher temperature equipment, and metal gaskets can be used for high temperature and high pressure equipment. The gasket type mainly has a flat gasket with a rectangular cross section and an O-ring with a circular cross section. Gaskets are often manufactured from a single material or composite material, such as an anti-corrosive PTFE-coated asbestos rubber gasket and a flat gasket that enhances the strength of the gasket or the outer foil. [1]
Seals used on high pressure vessels or equipment with a working pressure of 10 to 100 MPa are often referred to as high pressure seals. The high pressure seal has two types: forced seal and self-tight seal. Forced sealing is primarily used on high pressure equipment with a diameter of less than 1000 mm, a pressure of less than 20 MPa or a diameter of less than 600 mm and a pressure of less than 32 MPa. The flange gasket type forced seal relies on the preload of the bolt to press the gasket. When the equipment is working, the internal pressure of the container reduces the pressure on the gasket, but there should be sufficient pressure to ensure the seal. High pressure seals often use harder, narrower metal gaskets. When a self-tightening seal (Fig. 2) is adopted, the sealing pressure of the compression gasket comes from the locking bolt and the sealed medium. The greater the medium pressure, the better the sealing performance. The newer self-tightening seals have a metal C-ring seal and a metal O-ring seal. The C-ring seal relies on a convex arc to contact the cap and the cylinder, and the contact area is small. When the top cover is locked, the contact surface creates a large pressure to ensure a seal. When the pressure of the medium rises, the inner cavity of the C-ring is compressed, generating axial tensile tension, increasing the pressure of the sealing surface and improving the sealing ability. The C-ring seal has a simple structure, small pre-tightening force, convenient disassembly and assembly, and reliable sealing. It is mostly used in applications where the diameter is less than 1000 mm, the temperature is lower than 200 ° C, and the pressure is lower than 35 MPa. O-ring seals are available in both inflatable and self-tightening versions. The gas-filled ring is filled with an inert gas, and the gas pressure in the ring increases as the working temperature rises, thereby improving the sealing ability, and it is suitable for occasions with a high working temperature. There are small holes on the inside of the self-tightening ring.
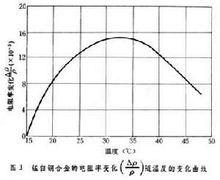
Static seal
Working pressure in the ring during operation can enhance the sealing ability. O-ring seals can form axial and radial self-tightening capabilities, sealing performance is very good, sealing pressure can reach 2800 atmospheres. Medium and low pressure static seals are usually soft and wide gaskets. As long as the pressure of the gasket contact surface exceeds the pressure of the sealing medium, the seal can be ensured. Liquid sealants can also be applied to the sealing surface in medium and low pressure equipment to provide a sealing action, which is called a liquid glue seal. The liquid sealant is a viscous liquid at normal temperature. After being dried on the joint surface for a certain period of time, it forms a film with adhesiveness, viscoelasticity or peelability. The filling effect of the film can seal the joint portion. The base of the liquid sealant is synthetic resin, synthetic rubber or natural polymer material. Liquid sealant such as heat resistance, cold resistance, pressure resistance, oil resistance, water resistance and chemical resistance can be prepared by adding appropriate amount of plasticizer and softener, filler, solvent and other auxiliary agents to the base material. Liquid sealants are also used to seal pipe threads, package miniature electronic components, protect instrumentation, and seal aircraft cockpits. [1]

Reference material
1. Detailed explanation of static seal. Baidu Library [reference date 2017-10-03]
Science Encyclopedia Engineering Technology Classification